To use Microsoft SQL Server with AMPL, you need to have the ODBC driver for SQL
Server installed and to have access to a database server, which could be either
local or remote.
Usage
We’ll demonstrate usage of MS SQL Server with AMPL on a small example.
For this example we use the diet problem, which finds a combination of foods
that satisfies certain nutritional requirements. It is described in
Chapter 2 of the AMPL book.
We assume that you’ve already installed the MS SQL Server ODBC driver using
the instructions above and have access to a local SQL Server database.
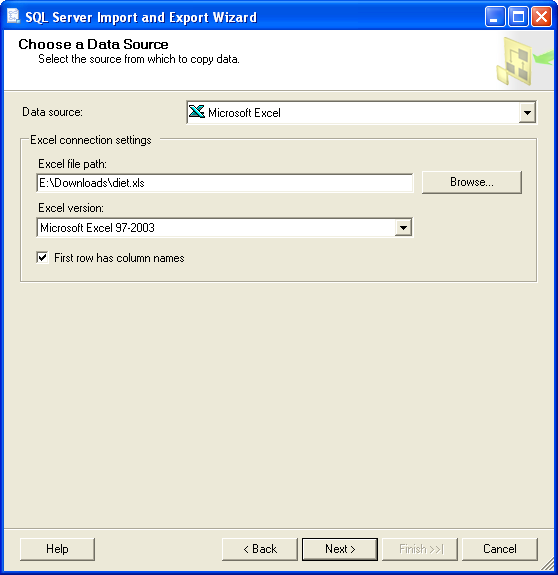
First download the data for the diet problem diet.xls and import it using the SQL Server Import and
Export Wizard
which can be run from the Start menu -> All Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server
-> Import and Export Data. Skip the Welcome page, if any, by clicking Next,
then choose Microsoft Excel as a Data source and specify the path to
the downloaded diet.xls file in Excel file path:
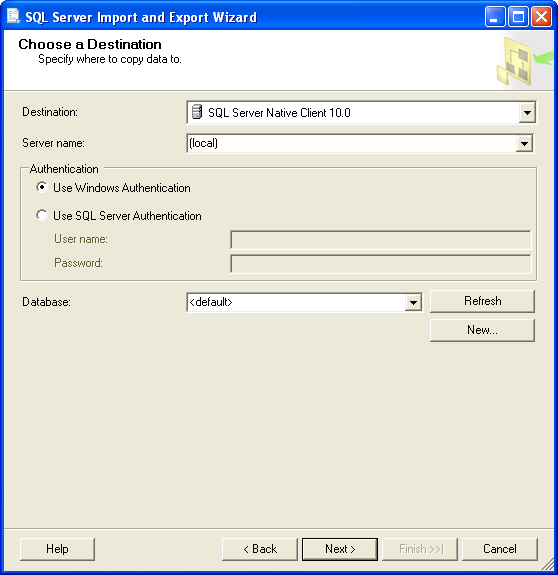
Click Next and on the following page provide the connection settings for the
SQL Server database you are going to use:
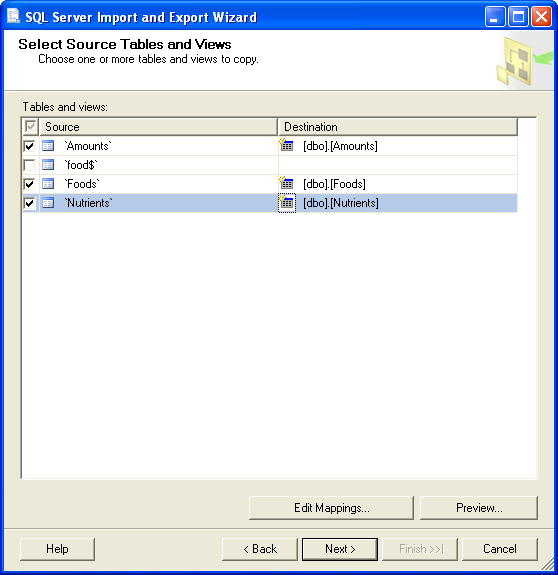
Click Next, select Copy data from one or more tables or views on the next
page and click Next again.
Select tables Amounts, Foods and Nutrients for import and click
Next:
Select Run immediately and click Finish on the next page and the one that
follows.
Once import is complete, download the model file diet.mod and the script file diet-sqlserver.run.
The script file first reads the model:
Then it defines a parameter to hold a connection string. Since the connection
parameters are the same for all table declarations in our example, we
avoid unnecessary duplication. In this case we specify all the connection
parameters explicitly. Alternatively, you could use a DSN file name or
"DSN=<dsn-name>" as a connection string.
param ConnectionStr symbolic = "DRIVER={SQL Server}; SERVER=(local);";
If you are using Linux and have chosen a driver name other than SQL Server,
you will have to specify this name instead of SQL Server in the
DRIVER={SQL Server} attribute in the connection string.
You can use a different version of the ODBC driver for SQL Server on Windows
as well. The driver name is chosen automatically during installation on Windows,
so if you are using this OS, you will have to find the driver name and
specify it instead of SQL Server in the connection string.
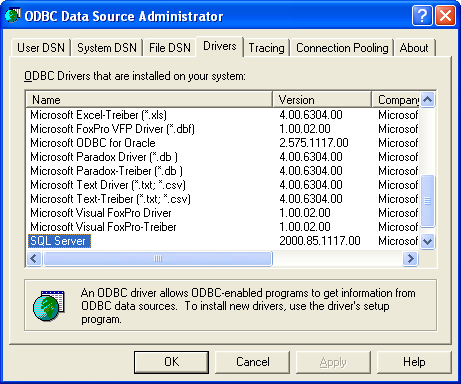
To discover the driver name on Windows, run the ODBC Data Source
Administrator, odbcad32.exe. Go to the Drivers tab where all the
installed drivers are listed and look for the one containing SQL Server:
A driver name containing a semicolon (;) should be surrounded with
{ and } in a connection string, for example:
param ConnectionStr symbolic = "DRIVER={SQL Server; version 11.0};";
Next there are several table declarations that use the ConnectionStr
parameter defined previously:
table dietFoods "ODBC" (ConnectionStr) "Foods":
FOOD <- [FOOD], cost IN, f_min IN, f_max IN,
Buy OUT, Buy.rc ~ BuyRC OUT, {j in FOOD} Buy[j]/f_max[j] ~ BuyFrac;
table dietNutrs IN "ODBC" (ConnectionStr) "Nutrients": NUTR <- [NUTR], n_min, n_max;
table dietAmts IN "ODBC" (ConnectionStr) "Amounts": [NUTR, FOOD], amt;
Finally the script reads the data from the tables
read table dietFoods;
read table dietNutrs;
read table dietAmts;
solves the problem
and writes the solution back to the database:
Note that the same table dietFoods is used both for input and output.
Running the diet-sqlserver.run script with ampl shows that data connection
is working properly and the problem is easily solved:
> ampl diet-sqlserver.run
MINOS 5.51: optimal solution found.
13 iterations, objective 118.0594032
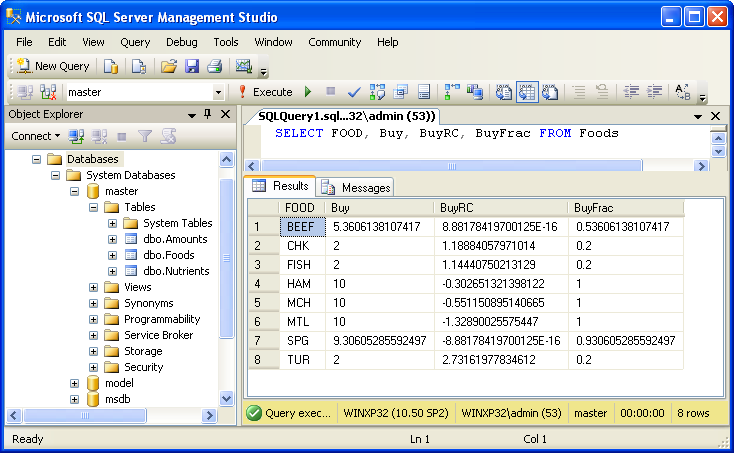
You can use various database tools such as SQL Server Management Studio to view the data
exported to the database from the AMPL script: